RedCap/eRedCap for IOT – GSMA Whitepaper
This is a whitepaper of the GSMA 5G IoT Community.
Link to the full GSMA white paper is here.
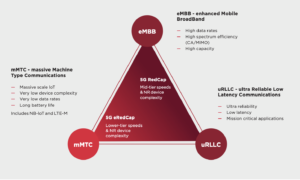
The initial 5G 3GPP Release (Release 15) targeted applications in three service categories – enhanced mobile broadband (eMBB), ultra-reliable low latency communications (uRLLC) and the low-throughput and battery-efficient massive machine-type communication (mMTC), as defined by the ITU Radiocommunication Sector’s IMT-2020 specification. After the commercial roll-out of numerous 5G networks across the globe, a need has emerged for a variant of 5G in which the performance and costs are optimised for use cases that fall in-between these initial service categories. To fill this gap, 5G RedCap (Reduced Capability1 ) was introduced in 3GPP Release 17 as a 5G variant (see Figure 1), and was followed by the even leaner 5G eRedCap (Enhanced Reduced Capability), specified in Release 18. Mobile network operators (MNOs) can now service the full spectrum of IoT use cases with the 5G standard, including those applications which are either too demanding to implement with the low power wide area (LPWA) connectivity of 5G mMTC (NB-IoT and LTE-M), or too basic for the over-performing eMBB and uRLLC capabilities of 5G New Radio.
 b
b
Figure 1. RedCap/eRedCap positioning against 5G use case groups defined in IMT-2020
RedCap and eRedCap are based on the 5G standalone (SA) architecture, and can thus convey a multitude of benefits to IoT applications, such as:
— Higher peak data rates: Superior data rates are offered than mMTC, comparable to lower LTE categories, meaning 5G RedCap can support smart grid monitoring, video surveillance and other more demanding applications.
— Reduced latency: Round-trip delays are lower than, or match those, of LTE, enabling applications that require the near real-time exchange of data, such as industrial automation, wireless sensors, wearables and even low-end extended reality devices.
— Reduced power consumption: Improved power efficiency enables an extended lifetime in batterypowered devices. This is extremely important for devices, such as wearables or sensors, for which the original 5G NR consumes too much energy.
These enhancements, also come with a considerable reduction in device complexity and cost, making RedCap/eRedCap the new technology of choice for a range of IoT applications, such as: — Wireless industrial sensors: Monitoring and controlling remote equipment to improve efficiency and safety in industrial settings.
— Video surveillance: Transmitting real-time video feeds to improve security and deter crime.
— Smart grids: Monitoring and managing the power grid to help improve the efficiency and reliability of energy supplies.
— Smart wearables: Connecting wearable devices for lone workers, public safety officers, and assisted living, or health and fitness trackers.
Finally, 5G RedCap and eRedCap are well-positioned to play an important role in future IoT deployments, emerging as the primary migration path for services still communicating today over legacy 2G, 3G and 4G networks. As RedCap will only gradually become widely available, and roaming frameworks still to be put in place for global coverage, both RedCap and LTE will co-exist for a while, catering to the needs of the aforementioned IoT applications. The pace of technology migration will largely depend on individual MNOs’ strategies and some regions will adopt RedCap faster than others.

RedCap/eRedCap for IOT – GSMA Whitepaper
© GSMA 2025
